The pros and cons of government grants for home insulation in Canada can help homeowners understand how to maximize their savings on energy-efficient upgrades. These grants are designed to make insulating homes more affordable, contributing to better energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. While there are significant benefits, there are also certain limitations and requirements to consider. This article breaks down the key advantages and disadvantages of insulation grants in Canada, exploring eligibility, potential savings, and common challenges.
1. Pros of Government Grants for Home Insulation in Canada
Financial Savings
One of the most significant benefits of government grants is the financial savings they provide. These grants reduce the upfront cost of insulation upgrades, making it more affordable for Canadians to invest in improving their home’s energy efficiency. By lowering heating and cooling needs, insulation upgrades also lead to long-term savings on energy bills.
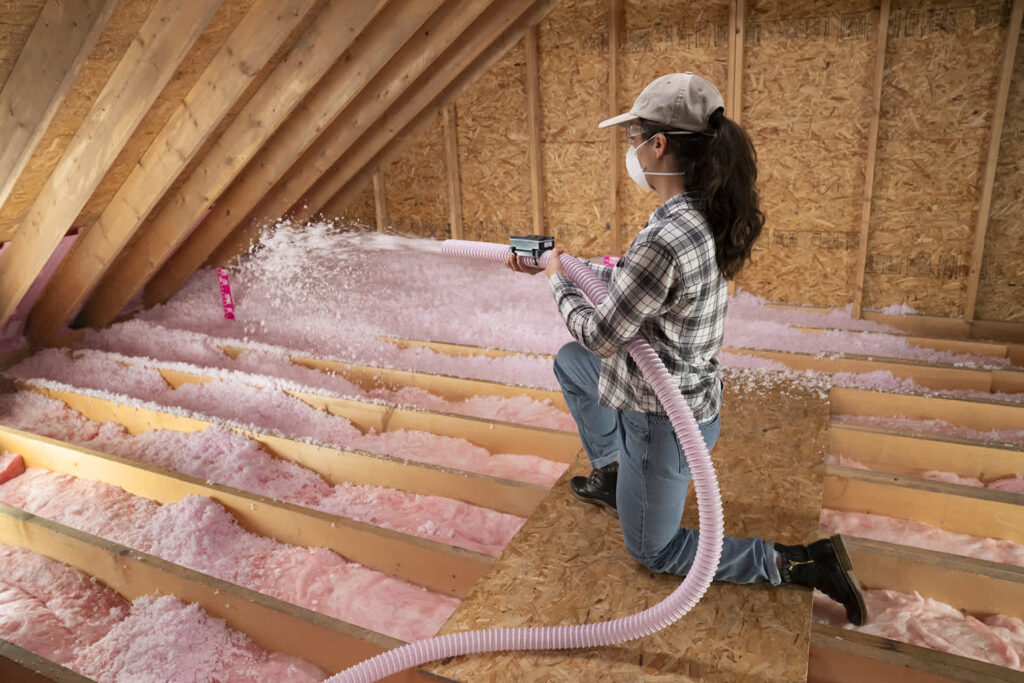

Increased Comfort
Better insulation enhances indoor comfort by reducing drafts and helping maintain a consistent indoor temperature throughout the year. Government grants enable homeowners to invest in high-quality insulation materials that increase their home’s ability to stay warm in winter and cool in summer, creating a more comfortable living environment.
Environmental Impact
Government insulation grants support Canada’s environmental goals by encouraging energy-efficient home improvements. Better-insulated homes use less energy for heating and cooling, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions. By making these upgrades more accessible, grants help homeowners contribute to a more sustainable environment.
Potential Increase in Property Value
Homes with energy-efficient upgrades, such as high-quality insulation, are often more attractive to buyers. The impact of insulation grants on home value can be positive, as energy-efficient homes are likely to see increased demand and higher resale values. This can be a considerable advantage for homeowners planning to sell their property in the future.
2. Cons of Government Grants for Home Insulation in Canada
Eligibility Requirements
A primary disadvantage of insulation grants is the eligibility criteria for Canadian insulation rebates. Most grants have specific requirements, such as income level, property type, or the need for an energy assessment by an approved advisor. These criteria can limit who qualifies, meaning some homeowners may not be eligible for funding.
Application Process Complexity
The grant application process for home energy upgrades can be complex and time-consuming. Homeowners typically need to undergo a detailed energy assessment, submit an application with required documentation, and follow specific guidelines for using approved contractors and insulation materials. This process can be overwhelming, especially for first-time applicants.
Partial Coverage
Many grants offer partial coverage rather than full funding for insulation upgrades. This limitation of energy efficiency grants can leave homeowners covering a portion of the costs on their own. While grants significantly reduce expenses, they may not eliminate them, which could be a drawback for some applicants.
Limited Availability and Funding Caps
Funding limits for eco-friendly home upgrades in Canada vary depending on the grant. Some programs have a set budget, which means funding may run out, leaving some applicants without assistance. Additionally, some grants impose caps on how much funding can be allocated per project or per household, limiting the extent of the upgrades.
3. Eligibility Criteria and Restrictions
Most insulation grants have specific requirements for insulation grant approval. Common requirements include a pre- and post-installation energy assessment, use of approved materials and contractors, and completion of work within a specified timeframe. Grants may also be restricted to primary residences, with vacation homes or rental properties often excluded from eligibility.
Typical Eligibility Requirements:
- Homeownership: Most grants are available only to homeowners, not renters.
- Energy Assessment: An assessment by an approved energy advisor is often required.
- Property Type and Use: Some grants apply only to primary residences, not secondary or rental properties.

4. Challenges with Insulation Rebates
Applying for insulation rebates can come with several common challenges. Beyond eligibility and application complexity, the popularity of these grants can lead to long wait times for assessments and approvals. Additionally, grant requirements such as using approved contractors may limit homeowners’ options, potentially increasing costs or delaying project timelines.
5. Effectiveness of Insulation Incentives in Canada
Despite the challenges, the effectiveness of insulation incentives in Canada is generally positive. These grants have helped countless homeowners improve their home’s energy efficiency, leading to substantial savings on utility bills and a more sustainable living environment. For those who qualify and can complete the application process, insulation grants offer valuable support in making eco-friendly upgrades.
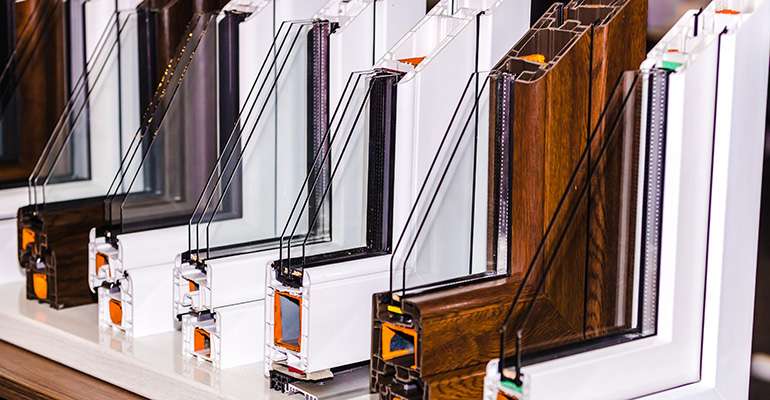
Comparison Table: Window Materials for Insulation Efficiency
Choosing the right window materials can further enhance a home’s insulation and energy efficiency. Here is a comparison of popular window materials and their insulation properties:
| Window Material | Energy Efficiency | Durability | Maintenance | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | High | High | Low | Cost-effective, energy-efficient solution for modern homes |
| Wood | Moderate | Moderate | High | Suitable for traditional homes, adds aesthetic appeal |
| Aluminum | Moderate | High | Low | Durable, ideal for contemporary designs needing resilience |
| Fiberglass | Very High | Very High | Low | Premium choice for homes focused on maximum energy savings |
Choosing the Best Window Material
- Vinyl: Energy-efficient and affordable, vinyl windows are a practical option for homeowners looking to improve insulation on a budget.
- Wood: Although it requires higher maintenance, wood offers a classic look and is popular in historic or traditional homes.
- Aluminum: Known for its durability and sleek design, aluminum windows are ideal for contemporary homes but offer moderate insulation.
- Fiberglass: Offers superior insulation and durability, making it a great choice for those focused on energy efficiency.

Conclusion
Understanding the pros and cons of government grants for home insulation in Canada helps homeowners make informed decisions about energy-efficient upgrades. While these grants provide substantial financial assistance and contribute to a greener environment, it’s important to consider the eligibility requirements, application process, and potential funding limitations. For those who qualify, these grants are an excellent resource, making it easier to invest in sustainable, comfortable, and energy-efficient homes. Whether you’re planning to upgrade insulation or replace windows, government support can be a valuable part of your home improvement journey.




